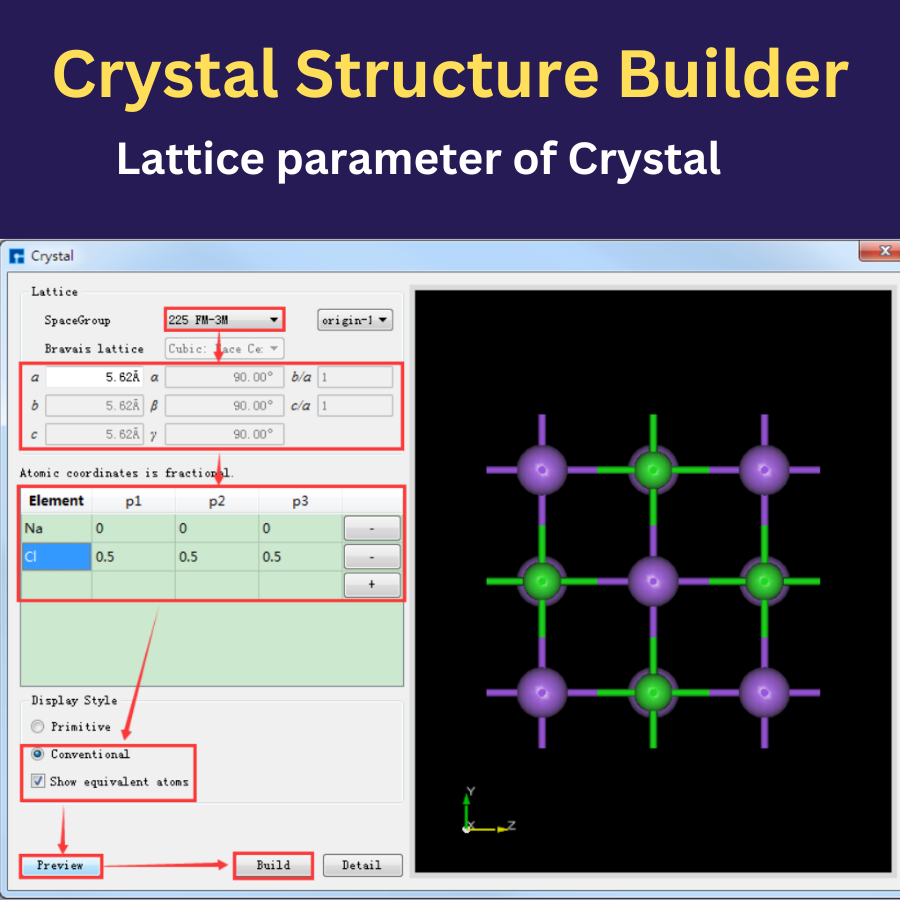
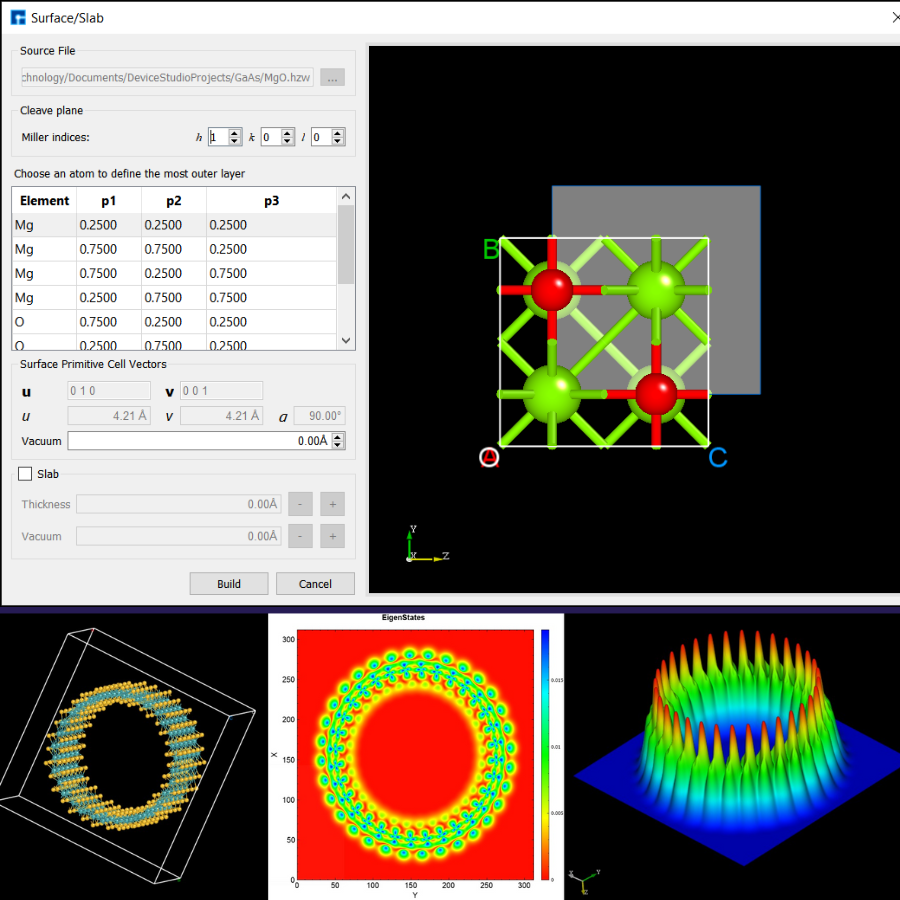
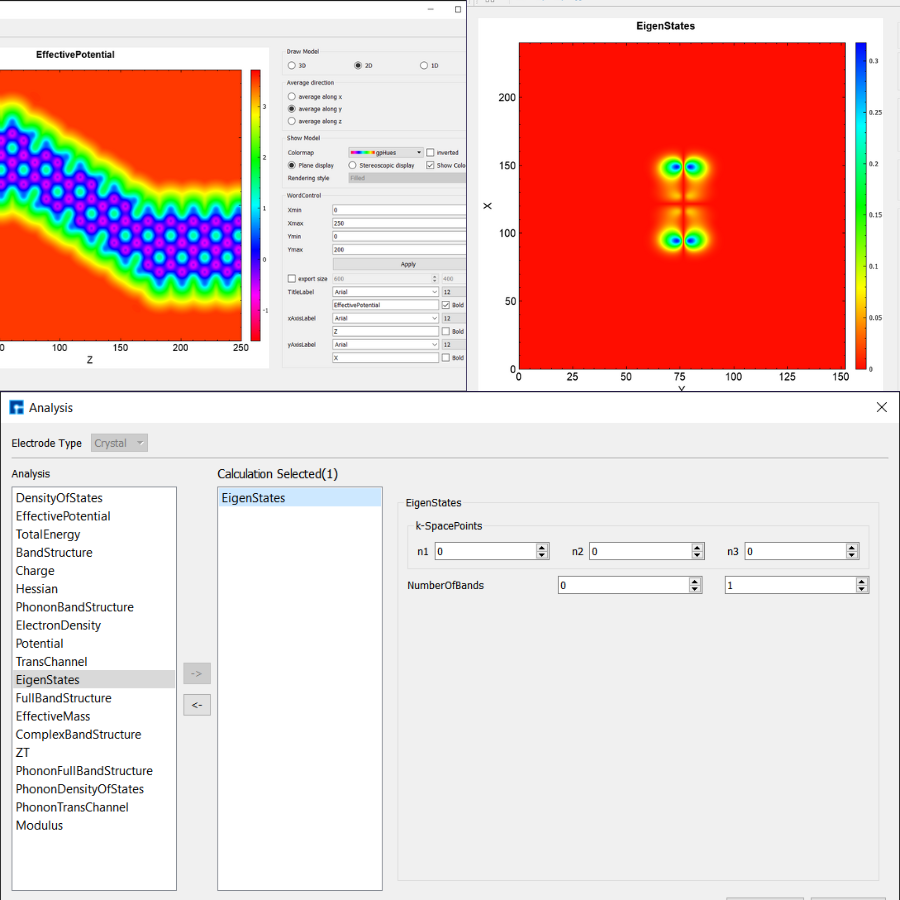
NanoDCAL is a state-of-the-art first principles quantum transport package, combining the nonequilibrium Green’s functions (NEGF) formalism with density functional theory (DFT) that predicts nonequilibrium quantum transport in nanostructures.
Physical and chemical properties of materials based on the spin-dependent states (collinear) in ferromagnetic (FM) or anti-ferromagnetic (AFM) configurations, the Kohn-Sham single-particle wave functions are represented as products of spatial orbitals with up- or down-spinors. The magnetic moment from the system is collinear with spin quantization axis. The first-principles density functional theory (DFT) with the local density approximation combined with the nonequilibrium Green’s function (NEGF) formalism as implemented in the NanoDCAL.
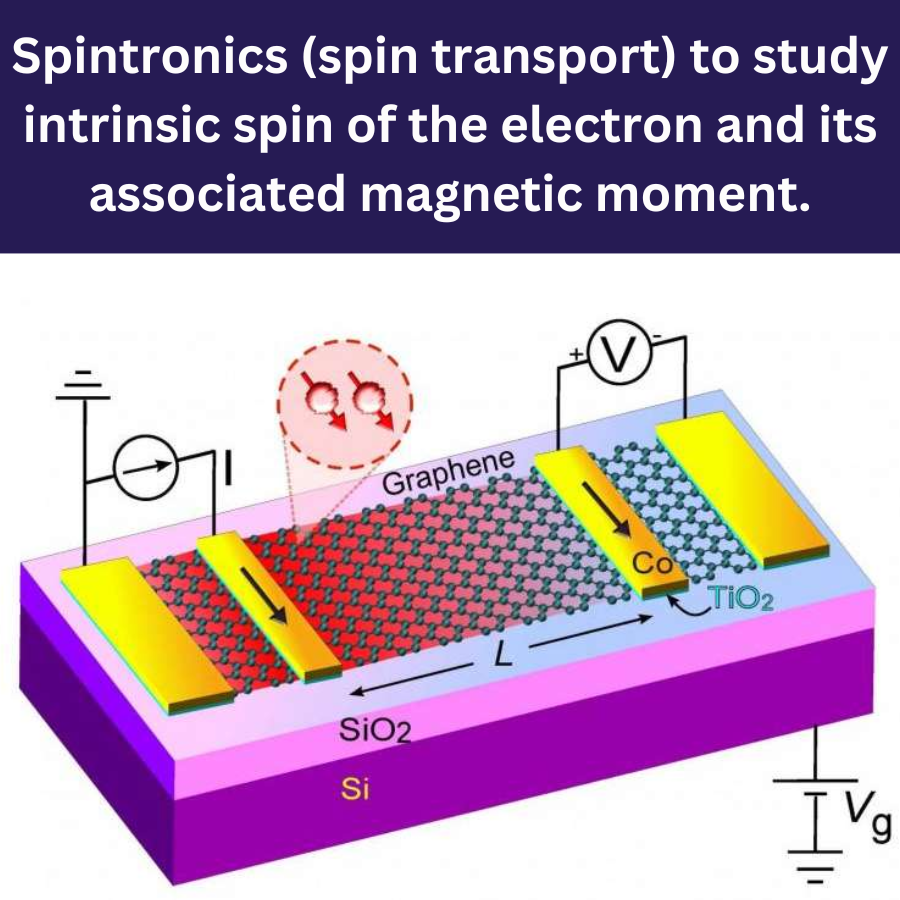

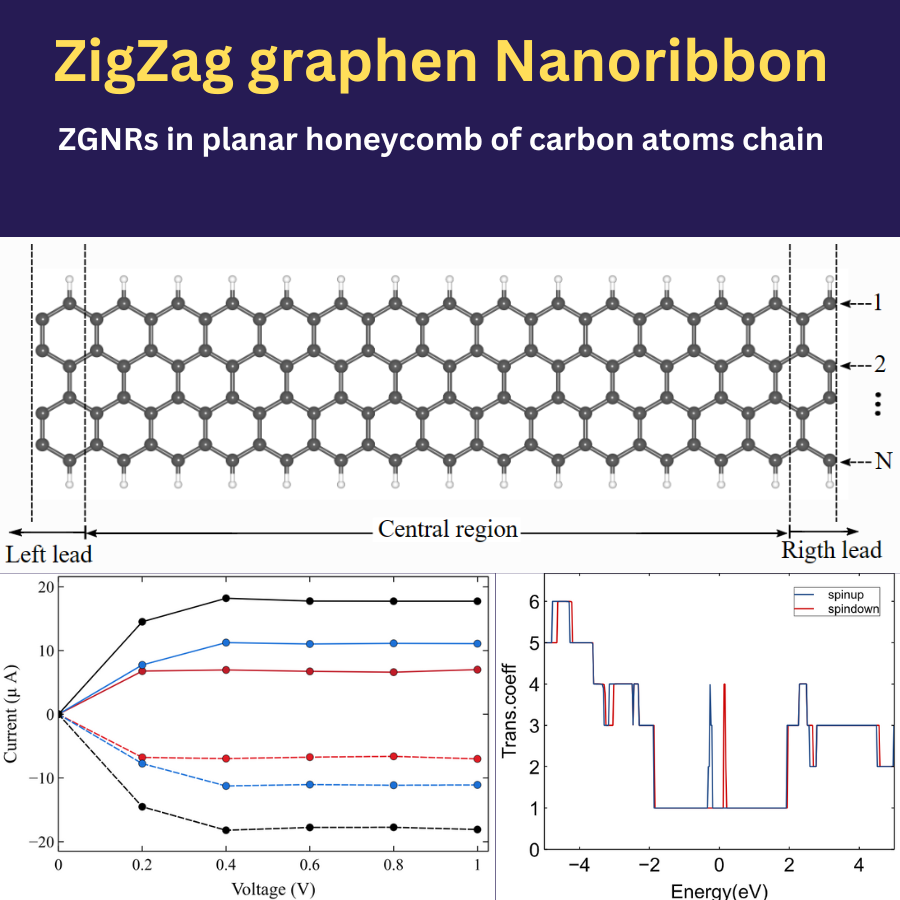
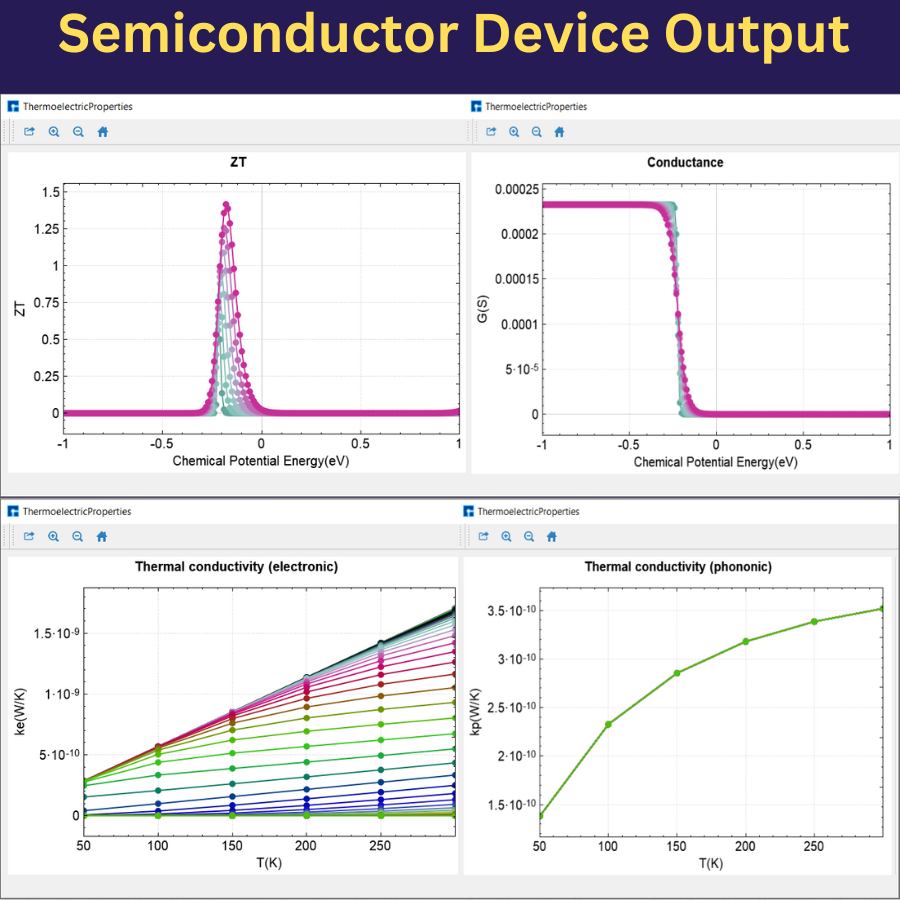
Semiconductors are an amazing class of materials with tunable electrical conductivity. The advances in semiconductor technology are devoted to exploring these materials to convert them into carefully-designed functional devices with the targeted electrical and optical properties. The miniaturization of those devices becomes one of the main trends in the future semiconductor industry. These tutorials and videos focus on how to set and compute the outstanding physical-chemical properties of several semiconductors.
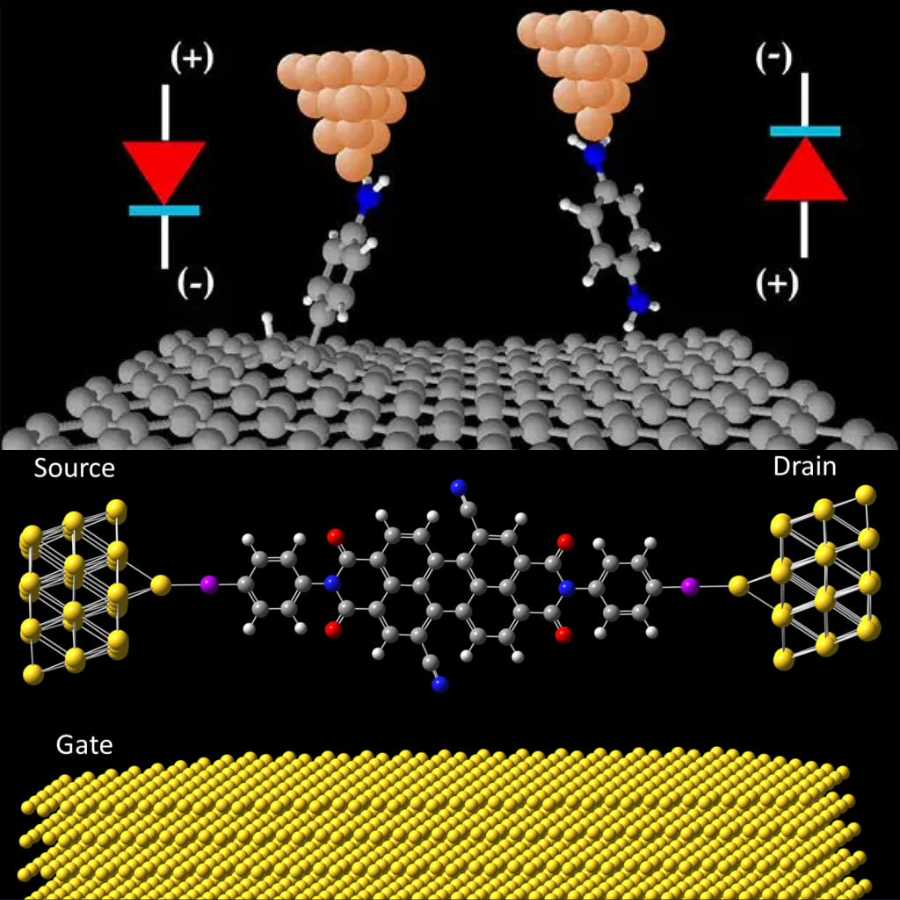
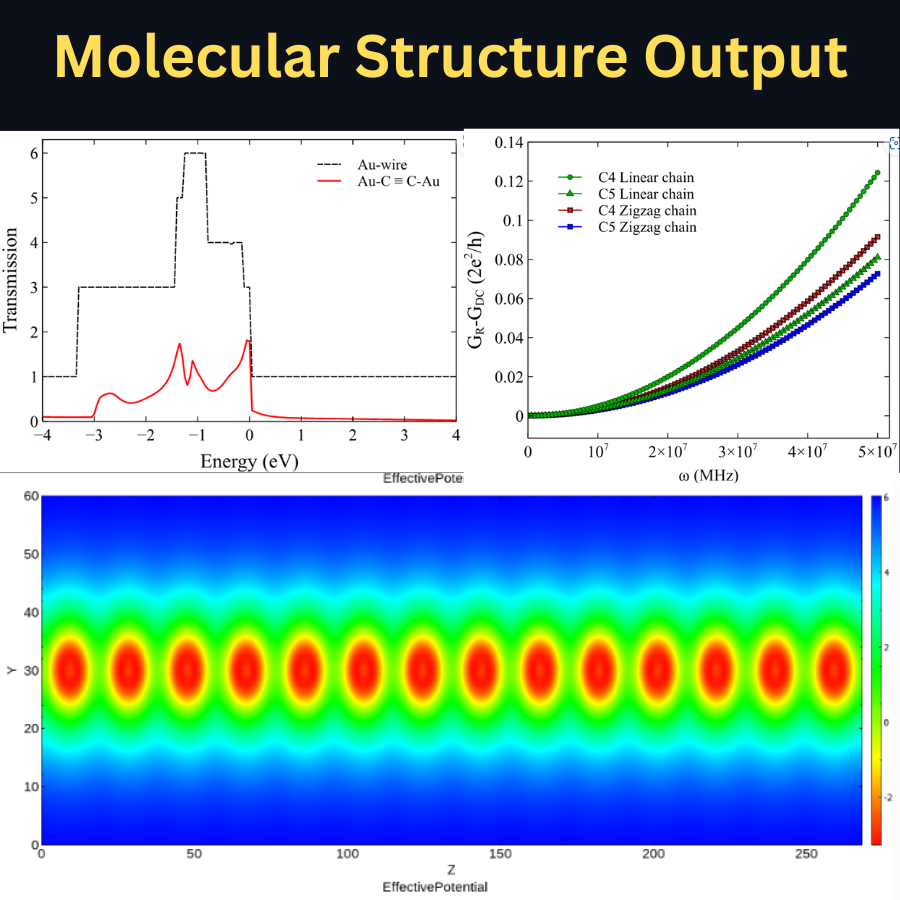
Molecular electronics is a field of study that deals with the design, fabrication, and application of electronic devices that are based on individual molecules or molecular assemblies. One of the main goals of molecular electronics is to develop devices that are smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient than conventional electronic devices. This is because molecules can be arranged in much smaller and more precise patterns than bulk materials.
Some of the potential applications of molecular electronics include:
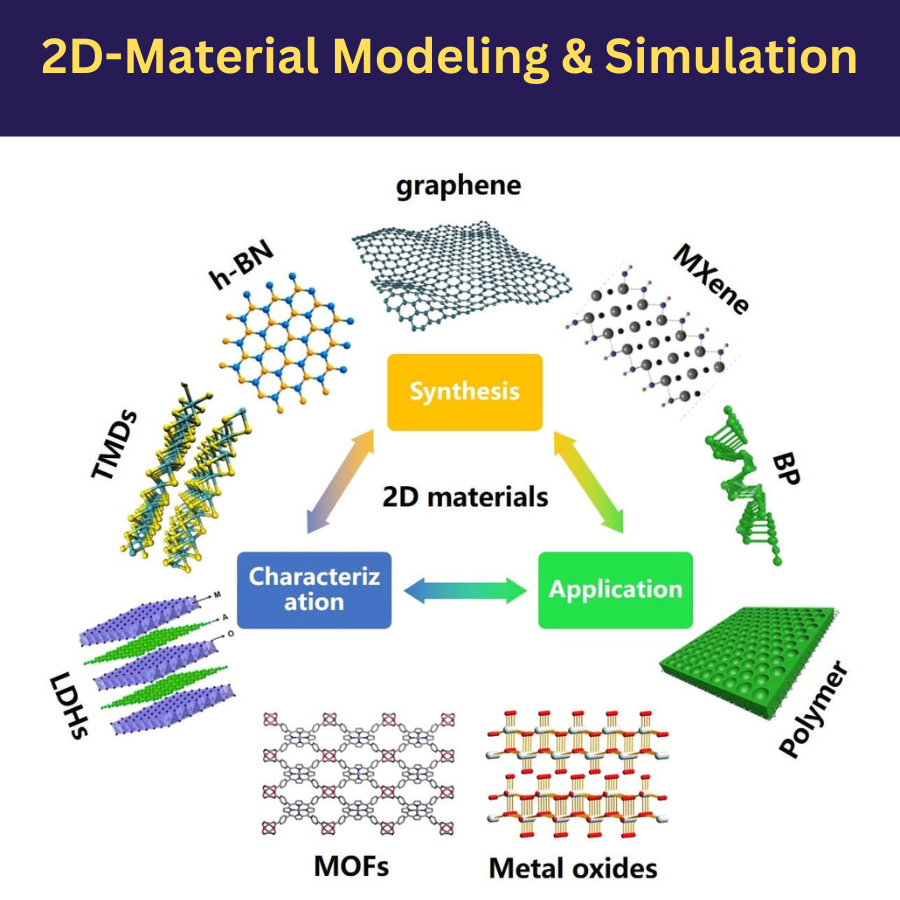
Two-dimensional (2D) materials can be defined as a crystalline structure that consists of a single- or few-layer of atoms. In fact, those materials can be described as a “hybrid” system of a solid (in the periodic plane) and a molecule (nonperiodic perpendicular direction). The atoms along the in-plane directions are strongly bonded by covalent or ionic interactions to form the atomic layer and the electrons are free to move throughout the plane. On the other hand, along the out-of-plane direction, these atomic layers are weakly held by van der Waals force, in that case, the movement of the electrons is restricted and governed by quantum mechanics.
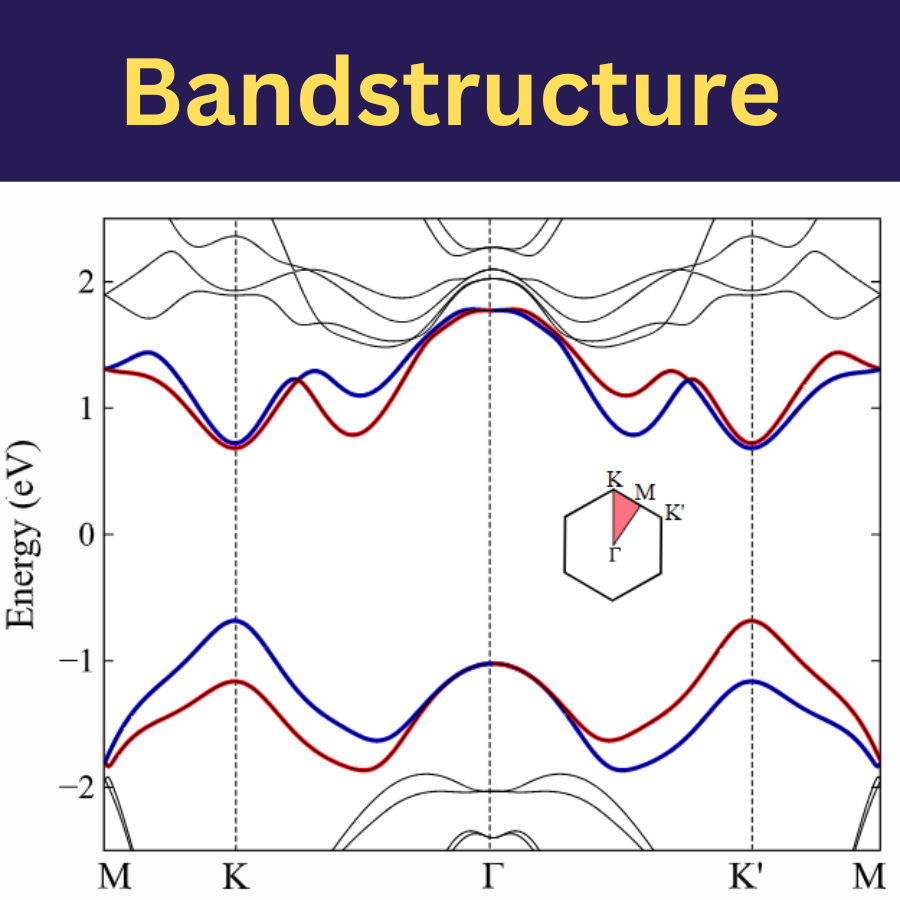
Material science and chemistry deal with the study of materials and their properties, structure, composition, and behavior. While material science focuses on understanding the structure-property relationships of various materials, chemistry delves into the composition, reactions, and behavior of substances at the molecular and atomic levels.